Conceptual Modeling
Conceptual modelling, also known as visualising, is an idea that only exists in mind or possibly on paper. It can help with:
- Grouping ideas
- Improving your design thinking
- Bringing together parts of other products
Conceptual modelling can be complicated in the IA as it is hard to translate something in your head onto paper
|
Stage
|
Definition
|
Type
|
Definition
|
Tools
|
Graphical / Virtual Modelling
|
Graphical modelling is a visualisation of the idea in either 2d or 3d design.
|
Sketching
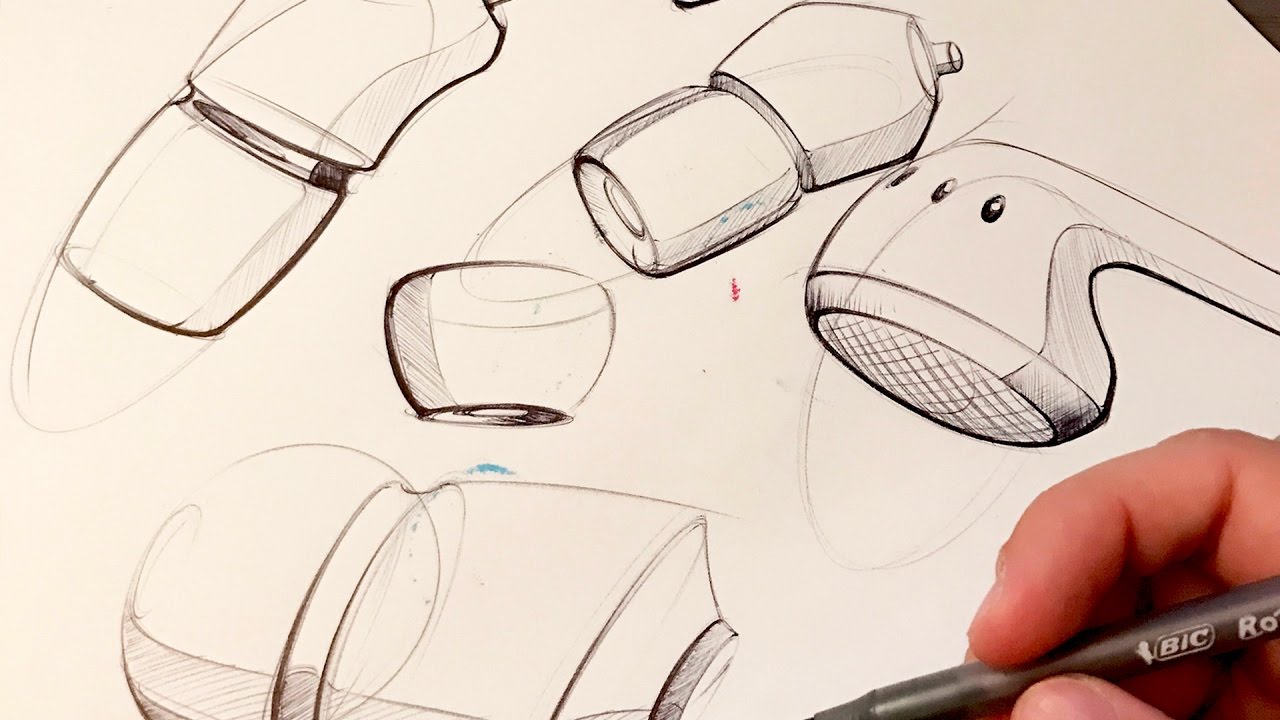

|
A rough and quick visualisation such as a diagram, or a rendered sketch.
|
Graphical - pen on paper with the aid of tracing materials. 1,2 or 3 points perspective or Isometric perspective.
or/and
Virtual (Digital) - CAD software on a computer like Solidworks and Fusion 360. In working drawings, it is critical to include dimensions.
|
|
Formal drawing
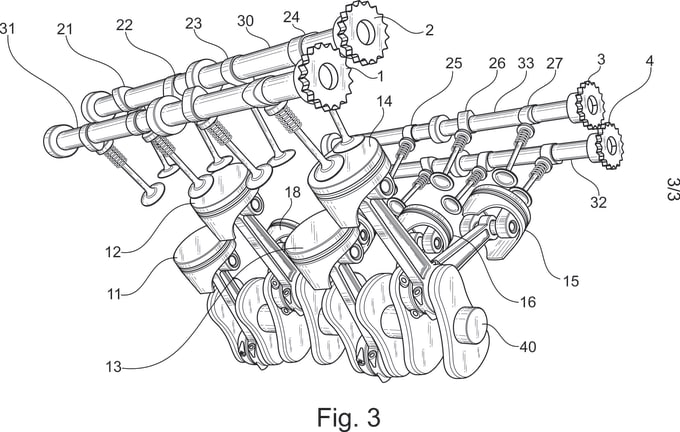
|
Detailed visualisation such as a flow chart, technical drawing. It must be to scale.
|
|
Virtual (2D, 3D)
|
The approximate representation used to communicate design.
|
|
Part, assembly and exploded drawings

|
Display of the different parts and how they come together. This can come in the form of a working drawing.
|
Physical
|
Physical modelling is a physical representation of the visualisation
|
Scale

|
Smaller or larger physical model
|
From simple foam board and glue to using proper manufacturing techniques
|
|
Aesthetic

|
The model used to assess the visual appeal
|
|
Mock-up

|
Full-scale model, used for tests and analysis
|
|
Prototype
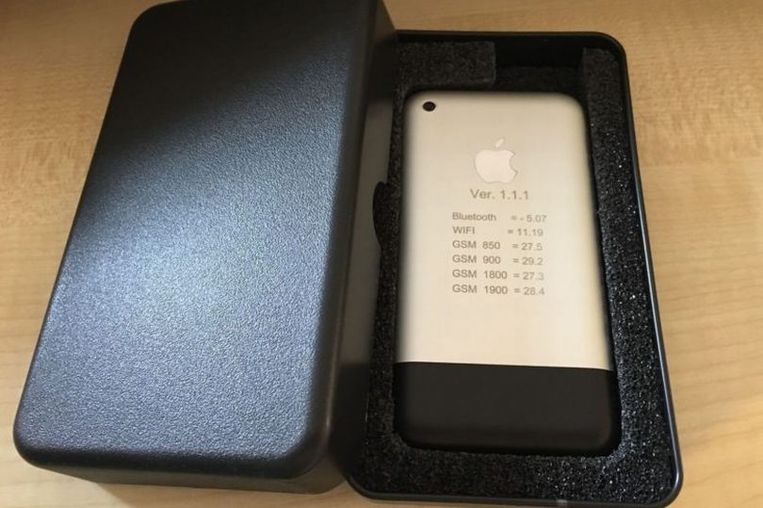

|
Final mock-up, before production
|
Virtual Modelling
Advantages:
- Helps to explain features
- Helps with project planning
- Gauges peoples reaction
- Promote Communication
Disadvantages:
- Make assumptions
- Too simplistic (Particularly drawings)
- It is sometimes hard to display scale (might be a good idea to have a reference object like a Rubix cube there for size)
- Graphical models can be difficult to follow
- If not made of final materials it can cause an adverse reaction
Physical Modeling
Advantages:
- Explore and test ideas
- Easily understandable
- Helps communicate with clients
- Helps communication with teammates
- Ability to manipulate ideas better
- Is tangible
- Can be used in user trials in more than one way
Disadvantages:
- A designer can make assumptions about how accurately a model represents reality
- It may not work as the final products
- Might be made of different materials
- Time-consuming
- Level of skill required
- Can be costly
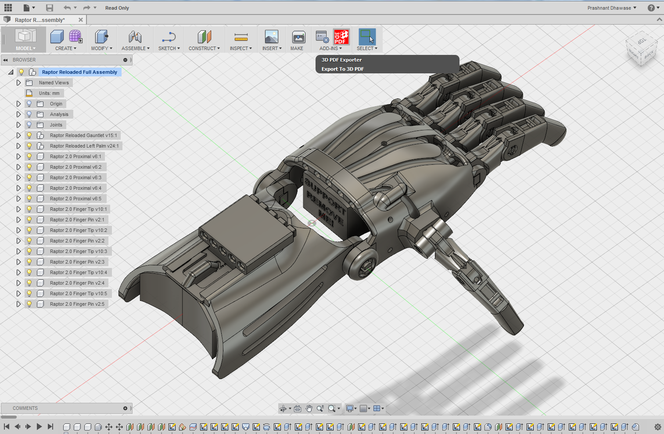
Virtual Prototyping - Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Advantages:
- Changes to ideas are quick and easy
- Communicate with the client easily
- Avoid costly mistakes
- Reduce costs as extra prototypes not needed
- Can be easily turned into a prototype of high fidelity
- Finite element analysis to test material capabilities eg stress and strain
Disadvantages:
- Software/hardware costs
- Special training and steep learning curve
- Mid-fidelity model
Digital Humans: Motion Capture and virtual reality
- Computer simulations of the biometrics of the human body
- help to predict how humans will react to tasks and environments
- digital humans can be used to repusent joint resistance
- capture and record how humans move and react
- Haptic Technology allows humans to interact with computer simulation focusing more on a sense of touch

Ranges of fidelity and context
The combination of the fidelity and context help designers develop concepts towards a final prototype.
|
Range of Fidelity
|
Description
|
Range of Context
|
Definition
|
|
Low
|
Conceptual representation - conceptual drawing - sketch - Not really tangible - the user can offer input into the design idea (Like a CAD model)
|
Restricted
|
Testing in a controlled environment (specific design brief)
|
|
Medium
|
Representation of aspects - formal picture - blueprints, mock-up
|
General
|
Trial with any user in any environment (less strict design brief)
|
|
High
|
As close as possible to the final product - prototype - allows full user interaction for testing
|
Partial
|
Testing with the final user (target audience) or environment
|
| |
Total
|
Testing with the final user and environment
|
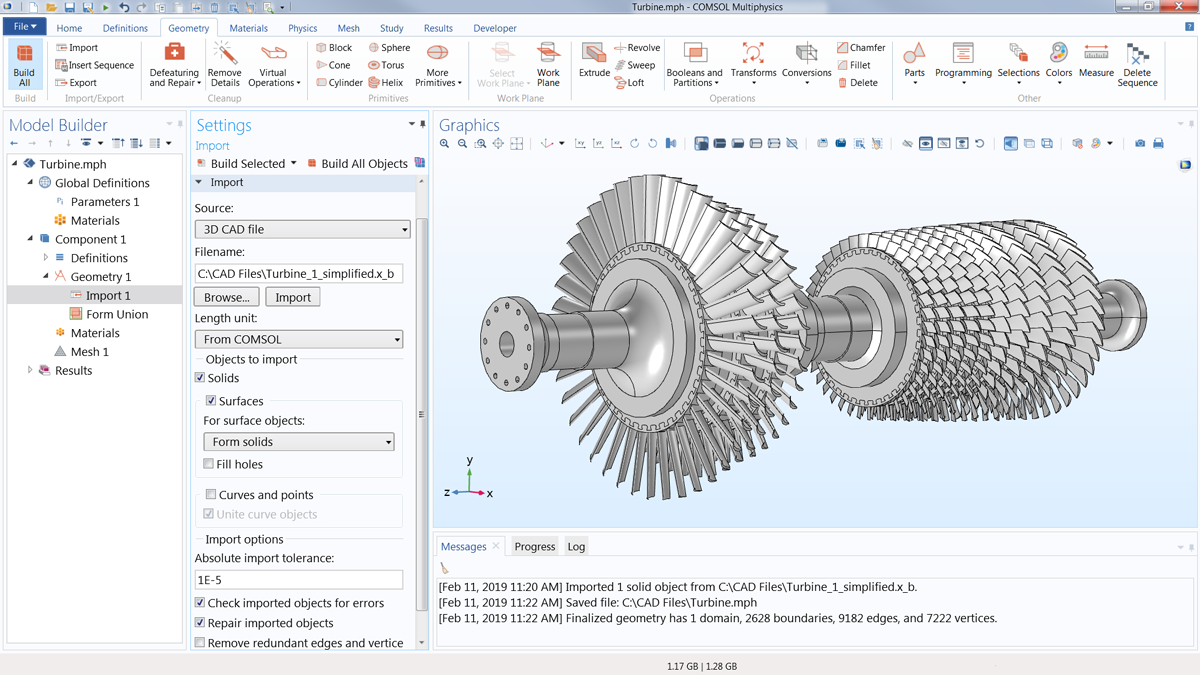
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Representation of the model
|
Term
|
Definition
|
Example
|
|
Surface
|
Digital aesthetic model made for the assessment of the exterior's visual appeal
|
A render of the facade of a building
|
|
Solid
|
Digital physical (size, volume ex.) representation of the final product
|
3D model of the shape
|
|
Data
|
A model containing all the data (structured data) and the fine details
|
Digital blueprints
|
Virtual prototyping
In 2019 CAD modelling can simulate products in different ranges of contexts (environments) to help enable better design.
Bottom-up vs Top-down strategy
Bottom-up modelling consists of multiple parts (geometries) that come together to create the product
Top-down modelling
consists of one component (geometry), creating the product in one body/shape
Digital Humans
Computer-based models of humans that contain various mechanical and biological properties and therefore allow designers to predict how a human body would react to a situation and environment. It will enable testing dangerous settings like car crashes without harming real humans.
Advantages
- Low cost - digital prototypes are cheaper to produce, and reduced compensation costs resulting from accidents,
- Safer products - enables to provide more accurate data for analysis and improvement
- Increased productivity - reduces the time spent of testing in different environments and situations, and removes inefficiencies
Editors- admin_andrei - 414 words.
- CD_FER - 392 words.
View count: 6252