Cost Theory
Short run Vs Long Run
Short run: Period of time in which at least one factor of production is fixed. All short run production takes place in short run (duration depends on fixed factors)
Long Run: All factors of production are variable but the state of technology is fixed. All planning takes place in the long run
For example:
Factors of production of restaurant
- Workers - Not Fixed, can hire more people easily
- Management - Not Fixed, can hire more people easily
- Land - Fixed can not change in short run
- Equipment - not fixed can go to a store to buy materials
- Raw Materials - not fixed
- Building - fixed in short run
Total, average and marginal product
- Quantity of labour: The labour force. Unit = V.
- Total product: total output that a firm produces using its fixed and variable factors in a given time period
- Average product: TP/V. Output that is produced on average by each of the variable factors
- Marginal product: Is extra total product produced with each extra unit of labour
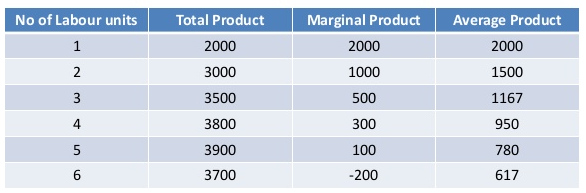
Law of Diminishing Returns
As extra units of variable factors are added to fixed factors, the output of the additional units of the variable factors will eventually diminish
Economics Cost
The economic cost of producing a good is the opportunity cost of the firms productions
- Explicit costs: purchased from others (need to pay for using it)
-
- Example: Buying materials for $10 000
- Implicit costs: Earnings a firm could have made. It is already owned by the firm (don’t need to pay for using it)
-
- Example using your own car for your business
Costs definitions
Average Costs: Costs per Unit of output
Total variable cost: price increase of each quantity
Total Costs: Variable Costs + fixed costs
Average fixed cost: TFC / Quantity (Always falls as output increases)
Average Variable Cost: TVC / Quantity (falls, then increases per unit, diminishing average returns)
Average total cost: TC / q
Marginal Costs: Change in TC / Q (the total cost of producing one extra unit of output). This cuts the AVC and ATC at their lowest points.
Example question: Manufacturing Signs. Machine costs 10 000 EUR. Materials for each sign is 7 EUR. 250 signs are produced.
- TFC = 10 000
- TVC = 7 x 250 = 1750
- TC = 10,000+1750 =11 750
Short run vs long run
MC cuts the AVC and ATC at their lowest points.
AFC (ATC-AVC) falls as output increases. The vertical gap between AVC and ATC gets smaller as output grows
Long run average cost curve
Long run average cost or envelope curve. Curve shows all possible combinations of fixed and variable factors
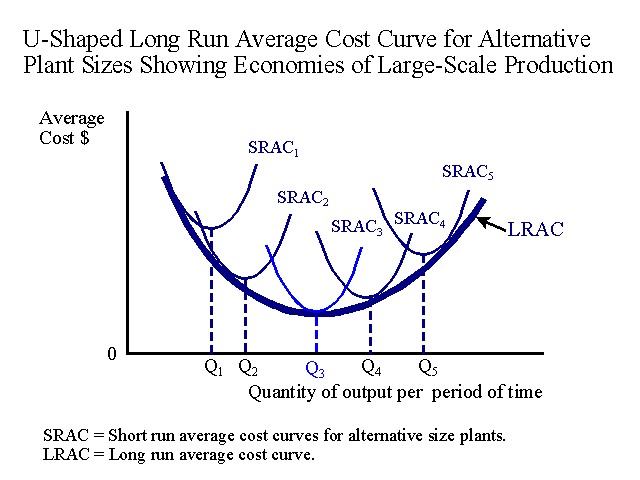
Returns to scale
Changes in output resulting from proportional changes in all input.
increasing returns to scale: cost decreases as output increases
Decreasing returns to scale: cost increases as output increases

Economies and diseconomies of scale
Economies of scale
Any decreases in the long run avg cost when a firm alters all of its factors of production
Causes:
- Specialization and division of labour- At large scales firms can have employees specialise in specific roles which they are best at.
- E.g In a small start up there may be one person who controls all of finance, but in a large company each small aspect will be specialised.
- Bulk Buying - buying more allows for negotiation of a lower price
- Financial Economies - easier for large company to take out money with less interest, due to relationships.
- Transport economies - same amount of energy to move more stuff, so cost per item is reduced.
- Large Machines - small companies can't justify large machines. Large machines can produce more for lower cost.
- Promotional economies - larger companies better at advertising. Just due to their size they will get enough advertising.
- E.g When the new iphone arrives, you likely know about it even if Apple didn't advertise it.
Diseconomies of scale
Any increases in the long run avg cost when a firm alters all of its factors of production
Causes:
- Control and communication problems - difficult for lower ranks to communicate with those in charge
- Alienation and loss of identity - working for a huge company makes you feel like you dont matter because you are one in a million.
Revenue Curve
Measurement of Revenue
- TR1 = Total revenue = p x q
- Ar = Average revenue TR / Q = p x q / q = p
- MR = Marginal revenue = Change in tr /change in q
Revenue curve and output for perfect competition
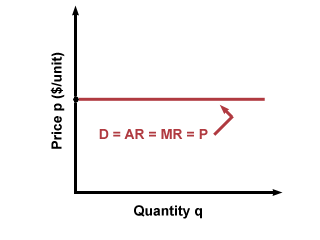
- Assume the firm is very small in relation to size of industry, so it can sell all its output and the quanity sold does not affect market price.
- Revenue when price falls as output t increases (downwards sloping demand) elasticity of demand falls as output increases) = if a firm wishes to sell more of its output and it can control the price at which it sells then it will have to lower the price if it wants to increase demand
Revenue maximisation
TR is maximized when MR = 0 and PED = 1
Profit Theory
Profit
Accountant vs economist definition of profit
Account profit = Total Revenue - total costs
Economist Profit = TR - Economic cost (explicit and implicit costs)
Types of profit
- Total revenue = Total cost : normal profit (zero economic profit) a good thing…
- Total revenue > Total cost : Abnormal profit l (economic profit) a better thing…
- Total revenue < Total cost : loss (negative economic profit) a less good thing…
Shutdown price, breakeven price, profit maximisation
- The shutdown price
-
- Has to do with Variable costs. If the variable costs exceeds revenue, then a firm has to shut down
- TVC = TR
- Break Even Price
-
- Has to do with normal profit. Where normal profit is made.
- Firm able to make normal profit in the long run
- Covering all its costs in the long run
- Price = Average total costs (all costs are covered)
- The profit- maximising level of output
-
- MC = MR
- Firm with perfectly elastic demand
- Firm with normal demand curve

Maximizing other goals
Profit maximisation is not always the goal of a company sometimes they care about maximizing growth or CSR.
- The revenue maximising level of output
- MR = 0
- Bigger market share, dominate market
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- People happier to work for a company if it’s not EVIL!
-
- Businesses includes the public interest in decision making
- Better workforce
- Reputation
- Brand Loyalty
- Ethical Consumerism
Editors- Nhf1185 - 2032 words.
- joeClinton - 82 words.
- DanyalWantensICS - 1055 words.
View count: 16074