Development
Poverty traps/poverty cycles
- Relative poverty – comparative level of poverty --> if they do not reach a specific level of income
- Depends upon where the specific level of income is set
- Absolute poverty – measured in terms of the basic necessities for survival --> level of income needed to buy items such as basic clothing, food & shelter
- If they are below a certain level
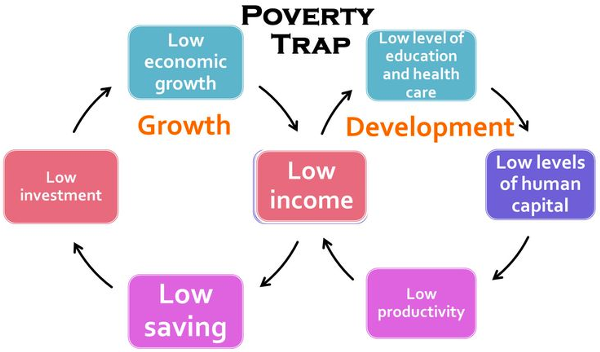
- Poverty cycle – development traps
- Single indicators – solidarity measures that may be used to access development
GDP & GNI per Capita
GDP per Capita - Total of all economic activity in a country regardless of who owns the productive assets, divided by the number of people in the population.
- Examples: income of foreign companies producing within a country would be included in the national income of that country but the activity of its own companies producing outside the country would not
GNI per Capita - total income that is earned by a country’s F.O.P regardless of where the asset is located divided by the number of people in the population.
--> IF the amounts of FDI are large, then GDP figures will be higher than GNI since GDP includes profits that may have been repatriated.
GDP per capita & GDP per capita at PPP (purchasing power parity)
- G&S don’t cost the same amount in different countries and thus purchasing power of a person’s income will be diff in diff countries
- Therefore the PPP exchange rate is used as it attempts to equate the purchasing power of currencies in different countries by comparing the prices of identical G&S in different countries
Health measures
- Life expectancy by birth
- Average number of years that a person may be expected to live from the time that they are born.
- Factors: level of health care & health care services; provision of clean water supplies & sanitation; provision of nationwide education; supplies of food; diets & lifestyles; levels of poverty; level of conflict.
- Infant mortality rate
- Measure of the number of deaths of babies under the age of 1 year per thousand live births in a given year
Education Measures
- Adult literacy rate
- Measure of the proportion of the adult population, aged 15 or over, which is literate expressed as a percentage of the whole adult population for a country at a specific point of time
- Influenced by the above factors + distribution of income within the country
- Net enrolment ratio in primary education
- Measure of the ratio of the number of children of primary school age who are enrolled in primary school, to the total number of children who are of primary school age in the country
Composite measures
- HDI
- Life expectancy at birth - Long and healthy life
- Education – adult literacy rate combined with a measure of primary, secondary and tertiary school enrolment
- Decent standard of living – GDP per capita
- HDI comparing with GDP per capita, we can make conclusions about the country’s success in translating the benefits of national income into achieving economic development.
- We cannot use only GDP per capita to measure development
- HDI is to reemphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country not economic growth
- Other indicators of development
- HDI is still an average figure that can mask inequalities within the country (e.g. inequalities between rural and urban citizens, between men and women, between diff ethnic groups)
- Gender related development index (GDI)
- Same indicators as HDI but takes into account the inequalities in these indicators for women and men.
- Gender empowerment measure (GEM)
- One aspect of development takes into account developing self esteem & creating opportunities & freedom for all people therefore it is valuable to measure whether development in a country is helping to create such freedoms and opportunities for women.
- Measures the extent to which women are able to actively participate in economic & political life + number & percentage of women in leadership, managerial & parliamentary positions & in technical & professional jobs. It examines the participation in the labour force & share of national income
- Human poverty index (HPI)
- Measure the level of deprivation & poverty
- Looks at the proportion of the people who are deprived of the opp to reach a basic level in each area
- Looks at indicators that are comparable with the HDI
- HPI is useful for observing how evenly the benefits of development are spread within the cotunry and is expressed as a percentage
- Genuine progress indicator (GPI)
- Measure whether a country’s growth (an increase in the output of G&S) has actually lead to an improvement in the welfare of the people
- To the GDP figures, it adds a non-monetary benefits such as the benefits of household work, parenting & volunteering work
- Given that economic growth generates many costs an indicator of GPI will deduct such costs:
- Environmental costs
- Resouces depletion
- Social costs – loss of leisure time, crime etc
- Commuting costs
- Costs of automobile accidents
View count: 3994