general knowledge
Key terms
|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Invention
|
A radical change in manufacturing, materials technology.
|
|
Innovation
|
Incremental change in manufacturing, materials technology.
|
|
Novel Product
|
Invention (new) which is unusual to existing products
|
|
Robust Design
|
A flexible design which adapts to changing technologies and markets |
|
Product family
|
Group of products with standard classification criteria (parts, aesthetics, and branding), usually from the same company
|
|
Market Analysis
|
The economic viability of a proposed design. Looking at viable costs, pricing, and essential.
|
|
Market Sector
|
A way of characterizing the markets
|
|
Market Segmentation
|
Dividing the market sector to specific groups of buyers (target audience)
|
|
Target Market
|
The people that buy your products
|
|
Target Audience
|
The people that consume your products
|
|
User Need
|
|
Stakeholders in invention and innovation
|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Lone Inventor
|
An individual creator who is not part of a company and is working on a novel product
|
|
Product champion
|
Individual within a company that supports ideas
|
|
Investor
|
financial backer |
|
Entrepreneur
|
An influential individual who brings insights into the market
|
Diffusion and Suppression
Diffusion
This is when a new design gets accepted by the market as if it’s always has been there.

Suppression
Suppression is when an idea is slowed down by the market as it has the potential of beating the competition
Invention
Drivers
-
The will to express one’s creativity or personal interest
-
Scientific/technological curiosity
-
Constructive discontent with current products
-
A desire to make money
-
A desire to help others

Intellectual Property
IP - a creation of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names, and images used in commerce. (from The World Intellectual Property Organisation)
|
Term
|
Sign
|
Definition
|
|
Patent
|
N/A
|
It provides the owner with the right to prevent copying, manufacturing, selling, or importing without permission.
|
|
Copyright
|
©
|
This protects the rights of artists and authors. This covers a wide range of products.
|
|
Trademark
|
™
|
A mark on a design (ex. name) which shows authenticity and protects the owner.
|
|
Servicemark
|
℠
|
|
Registered Trademark
|
®
|

Global Strategies
|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Market Penetration
|
Increasing sales to existing customers / finding new customers for an old product
|
|
Market Development
|
New applications for existing products
|
|
Product Development
|
Renewing products mainly for existing customers
|
|
Diversification
|
A company diversifying its family of products into other market sectors
|
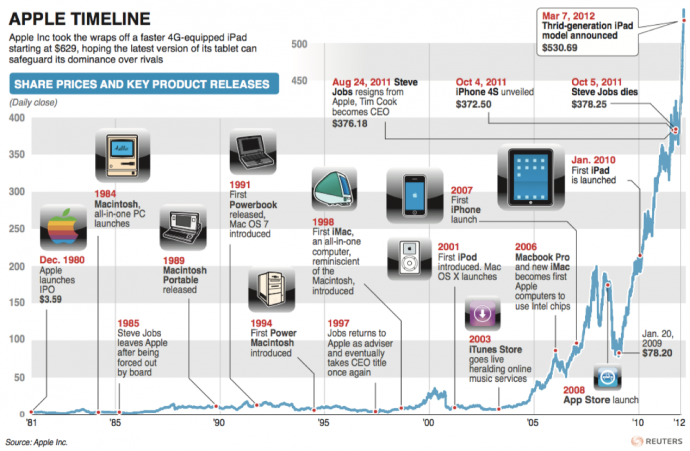
Innovation
Categories
|
Sustaining Innovation
|
Disruptive Innovation
|
Process Innovation
|
|
Meets consumer’s needs while supporting manufacturers
|
Challenges current technologies, setting a new standard for the market
|
Reorganization of the manufacturing process which may lead to reduced costs/benefits for consumers
|
Innovation Strategies for Design
|
Architectural Innovation
|
Modular Innovation
|
Configurational Innovation
|
|
Configuration of components to produce a new design
|
The ability to change critical elements, while the basic configuration stays the same
|
The combination of technological innovation and reorganization of components
|
| Moving the power button from top to side (phone) |
Improvements to the cameras (phone) |
The galaxy fold |
Strategies for Innovation
|
Strategy
|
Definition
|
Example
|
|
Adaptation
|
Adaptation of a physical solution from one context to another
|
|
|
Technology transfer
|
Transfer of advancements in technology from one context to another
|
|
|
Analogy
|
Transfer of an idea from one context to another
|
|
|
Act of insight
|
When an idea/solution comes suddenly, “eureka moment.”
|
|
|
Chance
|
An unexpected discovery, leading to a new idea
|
|
|
Technology push
|
When manufacturers/designers create the demand for the market
|
|
|
Market pull
|
When the market creates the demand for a new product
|
|
Stakeholders in Innovation and Design
| Stakeholder |
Roles |
Example |
| Product Champion |
- See's Value within the product
- Develop the product through all stages
- Keep the product in the consumer's mind.
|
Elon Musk, Steve Jobs, etc |
| Entrepreneur |
- Takes on the financial risk
-
|
|

Roger’s characteristics of innovation and consumers
Factors affecting the adoption of an innovation
|
Characteristic
|
Definition
|
Example
|
|
Relative advantage
|
The extent to which the innovation has an advantage over the previous ones
|
|
|
Compatibility
|
Consistency with current design interfaces and needs of the market/audience
|
|
|
Complexity
|
How easy or hard it is to use the product
|
|
|
Trialability
|
How easy it is to experiment with the market/audience
|
|

Category of consumers
| Consumer |
Definition |
Example
|
| Innovators |
The risk-takers that adopt the innovation as soon as it becomes available (introduction) |
Designers or the manufacturers themselves |
| Early Adopters |
The first wave of the consumers which add a product as soon as it comes out |
YouTubers or dedicated fans of technology |
|
Early Majority
|
More careful technology adopters which wait for feedback before purchasing a product |
The youth, anyone who would watch the YouTubers |
|
Late Majority
|
Adopters that wait for a product toe established in the marketplace |
|
| Laggards |
Late adopters which often wait for the product to decrease in price |
|

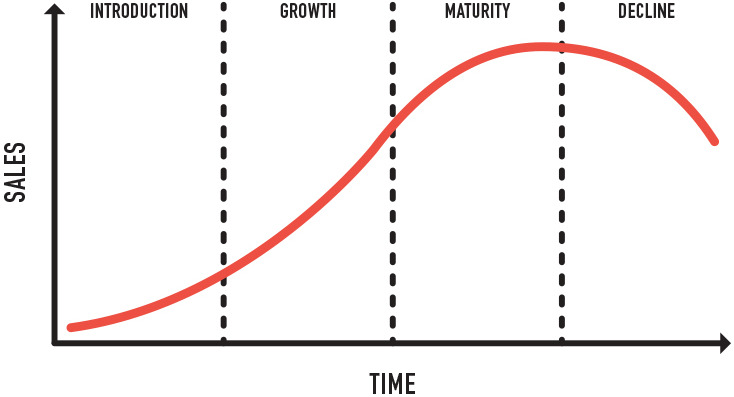
Product life cycle
|
Term
|
Definition
|
Example
|
|
Introduction (Launch)
|
Introduction of product to the market; high price, little profit, slow sales.
|
Apple Launch event, Advertisements, Galaxy Fold
|
|
Growth
|
Diffusion into the market; lowered price, increasing sales and profit
|
Electric Cars in 2020,
|
|
Maturity
|
Full acceptance of a product; medium cost, high profit, peak in sales
|
Smartphones
|
|
Decline
|
Market saturation; reduction of sales and profit, leading to lower price
|
Desktop Computers, Burner Phones
|
Sometimes things break the Product life cycle like this abomination (Supreme Burner Phone circa 2019):
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/65042649/supreme_feature_phone.0.jpg)
Obsolescence
Obsolescence is when an object becomes no longer wanted due to improvements in other products or no longer relevant.
|
Variation
|
Definition
|
|
Planned
|
An object purposefully becomes obsolete by gets replaced by the newer version of the same product from the same company.
|
|
Built-In
|
An object purposefully becomes obsolete by breaking down over a certain amount of time.
|
|
Fashion
|
As the name implies, it follows current trends and becomes undesirable after the style or fashion becomes outdated.
|
|
Functional
|
Mechanical properties breakdown and therefore become obsolete. |
|
Technological
|
New technology dramatically surpasses an existing one, rendering the old one undesirable (similar to Planned).
|

Editors- admin_andrei - 866 words.
- CD_FER - 230 words.
View count: 6369